
Introduction to AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, offering innovative solutions that enhance patient care, streamline operations, and improve clinical outcomes. AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from experience. In healthcare, AI is not just a futuristic concept—it’s a present-day reality with the power to revolutionize how medical professionals diagnose, treat, and care for patients.
From machine learning algorithms that assist doctors in diagnosing complex diseases to AI-powered tools that analyze vast amounts of patient data for predictive insights, AI is making healthcare smarter, faster, and more personalized. The use of AI technologies extends beyond the traditional realms of clinical applications to include administrative tasks, patient engagement, and drug development, driving both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness across the sector.
As the global healthcare industry faces challenges such as rising costs, a shortage of medical professionals, and an aging population, AI offers promising solutions. With the ability to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, AI not only aids in reducing human error but also helps healthcare providers make data-driven decisions, ultimately improving the quality of care patients receive.
This article explores the various ways AI is transforming healthcare, from revolutionizing diagnostics to enabling personalized treatments, and highlights the opportunities and challenges that come with integrating AI into modern medical practices. As we delve into real-world examples and emerging trends, it becomes clear that AI is not just a tool of convenience—it’s a game-changer for the future of healthcare.
Section 1: AI Technologies Transforming Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping the healthcare industry by applying cutting-edge technologies to improve patient outcomes, streamline medical processes, and enhance operational efficiencies. The core technologies driving this transformation include Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Below, we explore these technologies in detail and their impact on healthcare.
Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)
Machine Learning and Deep Learning are subsets of AI that enable computers to learn from vast datasets and make decisions or predictions based on patterns. In healthcare, these technologies have significant implications in clinical decision-making, diagnostics, and patient care management.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can analyze structured and unstructured data, making it possible for healthcare providers to identify trends, predict patient outcomes, and offer tailored treatment plans. For example, machine learning models are used to predict patient deterioration in real-time by analyzing historical patient data, vital signs, and medical history.
- Deep Learning (DL): A specialized form of ML that uses artificial neural networks to simulate human brain-like processing, deep learning is particularly effective in handling complex, large-scale datasets such as medical images and genomics data. Deep learning has been widely adopted in radiology to identify patterns in medical images (e.g., detecting tumors or fractures) and in genomics for predicting genetic disorders.
The combination of ML and DL enables healthcare providers to make more accurate and timely decisions, improving diagnosis accuracy and patient outcomes.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing allows computers to understand and process human language, making it an invaluable tool in healthcare, where large volumes of medical records, research papers, and clinical notes are generated daily. NLP helps to extract valuable insights from these documents and streamline medical workflows.
- Clinical Documentation: NLP can automatically extract important data from Electronic Health Records (EHRs), reducing the time clinicians spend on manual data entry and increasing the accuracy of patient records.
- Medical Research: NLP can analyze vast quantities of scientific literature and clinical studies to identify patterns or emerging trends in disease treatment. This is crucial for staying up to date with rapidly evolving medical knowledge.
- Patient Interaction: NLP also plays a role in improving patient engagement through AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants, which can help patients access information, book appointments, or manage their health.
By processing and analyzing textual data, NLP enables healthcare professionals to make data-driven decisions faster and more accurately.
Computer Vision
Computer vision involves the use of AI to interpret and analyze visual data, such as medical images, X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. This technology has become essential in modern diagnostic medicine, allowing healthcare providers to detect and diagnose diseases more efficiently.
- Medical Imaging: AI-powered computer vision tools can identify patterns in medical images that might go unnoticed by human eyes. For example, AI can be used to detect early signs of conditions such as cancer, retinal diseases, and neurological disorders by analyzing medical images with a high degree of precision.
- Surgical Assistance: AI can assist surgeons by providing real-time image analysis during surgery. This technology aids in precision surgery, helping to identify problematic areas in a patient’s anatomy, and ensuring optimal outcomes during procedures.
By automating image analysis, AI-powered computer vision not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also allows healthcare providers to handle larger volumes of imaging data, reducing workload and improving care delivery.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation refers to the use of AI to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that are traditionally performed by humans. In healthcare, RPA is primarily applied in administrative and operational tasks to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Billing and Coding: AI can automate the medical coding process, extracting relevant information from patient records and assigning the correct codes for insurance billing, reducing the chances of errors and speeding up claims processing.
- Claims Processing: RPA is used to automate the review of insurance claims, cross-checking claims against medical records and policies. This results in faster claim adjudication and fewer human errors, improving patient satisfaction and reducing administrative overhead.
- Appointment Scheduling and Patient Flow Management: AI tools help optimize appointment scheduling by automatically managing resources, predicting patient volume, and reducing wait times. This increases hospital efficiency and enhances the overall patient experience.
By automating routine tasks, RPA frees up time for healthcare staff to focus on more critical functions, improving both operational efficiency and the quality of patient care.

Section 2: Key Applications of AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence is making a profound impact on various facets of healthcare. By harnessing the power of data, machine learning, and predictive analytics, AI is improving the way healthcare providers diagnose, treat, and manage patient care. This section explores some of the key applications of AI in healthcare, showcasing how it is transforming diagnostics, treatment plans, disease prevention, drug discovery, and patient engagement.
AI in Diagnostics
AI technologies have become indispensable in medical diagnostics, enabling faster and more accurate detection of diseases. By analyzing vast amounts of medical data, AI helps identify patterns and abnormalities that may be overlooked by human clinicians, enhancing both the precision and speed of diagnosis.
- Medical Imaging: AI-driven tools are revolutionizing medical imaging by automating the analysis of X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and other diagnostic images. These systems use deep learning algorithms to detect early signs of diseases like cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders. For example, AI has been shown to outperform radiologists in detecting lung cancer in chest X-rays and identifying diabetic retinopathy in eye scans. AI can also reduce the time it takes to interpret images, allowing for quicker diagnoses and treatment decisions.
- Diagnostic Assistance: AI also serves as a second opinion for clinicians, providing support in diagnosing rare or complex conditions. For instance, AI algorithms are increasingly being used to diagnose conditions like rare cancers or autoimmune diseases by analyzing patient symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results. These systems can cross-reference data from numerous sources, improving diagnostic accuracy and helping doctors make informed decisions faster.
AI’s impact on diagnostics is not limited to imaging; its ability to analyze large datasets, including genetic and clinical data, is changing the way healthcare professionals approach patient diagnosis and care.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Plans
AI’s ability to analyze patient data and identify individual patterns is opening up new opportunities for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
- Tailoring Treatment Plans: AI models use data from a variety of sources, such as genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, to create personalized treatment plans for patients. For example, in cancer treatment, AI algorithms analyze genetic data to recommend targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective based on the patient’s genetic profile. This personalized approach not only improves treatment outcomes but also minimizes the risk of adverse reactions to medications.
- Predictive Analytics for Treatment Response: AI systems can predict how a patient will respond to certain treatments based on historical data and clinical studies. This allows healthcare providers to select the most effective therapies for each individual, improving the likelihood of successful outcomes. For example, AI-driven platforms can predict how cancer patients will respond to chemotherapy, helping doctors adjust treatment plans to increase efficacy.
By using AI to personalize treatment, healthcare providers can offer more effective and individualized care, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention
AI is playing an increasingly important role in disease prevention by identifying early warning signs and predicting the onset of chronic conditions. This predictive capability enables healthcare providers to intervene early, offering preventative treatments or lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of disease development.
- Chronic Disease Prediction: AI models are used to analyze patient data, including lifestyle factors, genetic predispositions, and environmental influences, to predict the likelihood of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or obesity. For instance, AI-powered tools can analyze patient records and identify patterns in risk factors, enabling doctors to provide early interventions, such as recommending changes in diet or exercise regimens, before the condition fully develops.
- Early Detection and Intervention: Predictive analytics in AI can also help identify early-stage diseases, allowing for timely intervention. For example, AI systems can detect early signs of cardiovascular disease or type 2 diabetes in patients before they exhibit obvious symptoms. Early diagnosis of such conditions can significantly reduce the need for more invasive treatments and improve long-term health outcomes.
AI-powered predictive tools are transforming the way healthcare professionals approach preventative care, focusing on early intervention and proactive management of patients’ health.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
AI is playing a critical role in accelerating drug discovery and development, making the process faster, cheaper, and more efficient. The traditional drug development process can take years, with high costs and high failure rates. However, AI is revolutionizing this process by automating the discovery of potential drug candidates and optimizing clinical trials.
- Drug Discovery: AI algorithms are used to analyze vast amounts of chemical, biological, and clinical data to identify potential drug candidates. AI can predict how different compounds will interact with biological targets, helping researchers identify promising candidates for further testing. For example, AI-driven platforms like BenevolentAI and Atomwise have been used to discover new molecules that can treat diseases such as Alzheimer’s, cancer, and COVID-19.
- Clinical Trial Optimization: AI also streamlines the clinical trial process by identifying the most suitable candidates for trials, monitoring patient responses in real-time, and predicting trial outcomes. AI can analyze patient data to select participants based on genetic, demographic, and medical criteria, improving the chances of trial success and reducing the number of participants needed. Additionally, AI can track real-time data from clinical trials, allowing for quicker adjustments to the treatment protocol.
By applying AI to drug discovery and clinical trials, the pharmaceutical industry is able to develop drugs more quickly and efficiently, potentially saving years of research and billions of dollars.
AI for Virtual Health Assistants
Virtual health assistants powered by AI are transforming the way patients interact with the healthcare system. These assistants can provide personalized care, answer patient inquiries, assist in scheduling, and even offer mental health support, all through natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning.
- Patient Interaction: AI-powered chatbots are increasingly used to handle routine patient interactions, such as appointment scheduling, reminders, and symptom checking. These virtual assistants help streamline administrative tasks, reduce wait times, and improve patient satisfaction. For example, platforms like Ada Health and Babylon Health use AI to provide patients with preliminary diagnoses based on their symptoms, offering advice on the next steps for treatment or seeking medical attention.
- Mental Health Support: AI-driven virtual assistants are also being used to provide mental health support. Platforms like Woebot and Wysa use AI to offer cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and emotional support to individuals dealing with anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions. These virtual assistants help bridge the gap in mental health services by providing instant, accessible, and confidential support.
AI-powered virtual health assistants offer significant potential to improve patient engagement, enhance accessibility to healthcare services, and reduce the burden on healthcare providers.

Section 3: AI in Healthcare Operations and Administration
In addition to its impact on clinical applications, AI is revolutionizing the administrative and operational aspects of healthcare. From automating routine tasks to enhancing resource management, AI is helping healthcare organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize workflows. This section explores how AI technologies are transforming hospital administration, electronic health records (EHR) management, and telemedicine services, contributing to an overall improvement in healthcare operations.
Automating Administrative Tasks
One of the most immediate applications of AI in healthcare is the automation of administrative and back-office functions. These tasks, while essential, are often time-consuming and prone to human error, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. AI technologies are helping streamline processes such as medical billing, coding, and insurance claim management.
- Billing and Coding: Medical billing and coding is a crucial but often tedious process. AI algorithms can automate the extraction of relevant data from patient records, applying the correct medical codes for procedures and diagnoses. This reduces the chances of billing errors, speeds up the process, and ensures compliance with industry standards. For example, AI systems can recognize patterns in medical claims, flagging potential issues and ensuring proper reimbursement from insurance companies.
- Claims Processing: Processing insurance claims can be complex and time-consuming. AI tools are now able to automate much of the process by cross-referencing claims with patient records, verifying eligibility, and ensuring that all required documents are submitted. This not only accelerates the claims process but also reduces administrative burden and minimizes human error, leading to faster reimbursements and improved financial performance for healthcare organizations.
By automating these routine tasks, healthcare providers can focus more on patient care and clinical decision-making, rather than spending valuable time on administrative duties.
AI for Hospital and Resource Management
Hospitals and healthcare facilities deal with a vast array of logistical challenges, including managing patient flow, optimizing bed usage, and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. AI is increasingly being used to optimize operations in real-time, improving hospital management and resource allocation.
- Patient Flow Optimization: AI tools help predict patient volume and manage hospital bed availability. For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze patient admission and discharge data to forecast the number of beds required in different units, reducing overcrowding and ensuring that patients are placed in the most appropriate care settings. By optimizing patient flow, hospitals can reduce wait times, minimize bottlenecks, and enhance the overall patient experience.
- Resource Allocation and Inventory Management: AI can also improve the management of medical supplies, equipment, and staffing. Machine learning algorithms can predict the demand for medical supplies, ensuring that healthcare organizations maintain appropriate stock levels while minimizing waste. Additionally, AI systems can assist in staff scheduling by analyzing patient volume, staff availability, and specific skill sets, ensuring that healthcare professionals are assigned to the right tasks at the right time.
By enhancing resource management, AI helps healthcare facilities run more smoothly, reducing operational inefficiencies and improving the quality of care delivered to patients.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Electronic Health Records (EHR) have become a cornerstone of modern healthcare, allowing providers to access and manage patient data more efficiently. However, managing the vast amount of information within EHRs can be challenging, especially as healthcare organizations collect more and more patient data. AI technologies are helping to optimize EHR management and make sense of the large volumes of data contained within these records.
- Streamlining Data Entry: AI can significantly reduce the time spent on manual data entry by automatically extracting key information from patient records. For example, NLP algorithms can scan clinical notes and transcriptions, converting them into structured data that is easier to analyze and retrieve. This reduces clinician burnout by allowing them to spend less time on administrative tasks and more time interacting with patients.
- Data Analytics for Decision Support: AI-powered analytics tools are helping healthcare providers unlock insights from EHR data to inform clinical decision-making. By analyzing large datasets from multiple patients, AI can identify patterns in patient conditions, track the progression of diseases, and provide recommendations for treatment options. These insights allow healthcare providers to make more informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.
- Reducing Errors and Enhancing Accuracy: AI can help identify discrepancies and potential errors in patient records, ensuring that data is accurate and up-to-date. For example, AI algorithms can flag missing or inconsistent information in patient charts, prompting clinicians to verify or correct the data before it impacts patient care.
With AI improving EHR management, healthcare providers can access critical patient information more quickly and accurately, leading to better-informed treatment decisions.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are two rapidly growing areas where AI is playing a transformative role. These technologies are helping healthcare providers extend care beyond the traditional clinical setting, offering patients greater convenience and access to healthcare services, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
- Telemedicine: AI is being integrated into telemedicine platforms to enhance virtual consultations and improve patient interactions. AI-driven tools such as virtual assistants and chatbots can help collect patient symptoms, conduct initial assessments, and even offer preliminary diagnoses. For example, AI-powered platforms like Babylon Health and Ada Health use machine learning algorithms to assess patient symptoms and provide guidance on the next steps, which may include scheduling a virtual consultation with a healthcare provider.
- Remote Monitoring: AI-powered wearable devices and mobile health apps enable continuous remote monitoring of patients, particularly those with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease. These devices collect real-time data on vital signs, such as heart rate, blood sugar levels, and blood pressure, and send the data to healthcare providers for analysis. AI algorithms can then analyze this data to detect any concerning trends or potential health risks, allowing for early intervention and reducing hospital readmissions.
By expanding access to care through telemedicine and remote monitoring, AI is helping bridge the gap in healthcare delivery, ensuring that patients receive timely interventions without needing to visit a hospital or clinic in person.

Section 4: Ethical Considerations and Challenges of AI in Healthcare
While AI offers enormous potential to revolutionize healthcare, its adoption comes with a host of ethical considerations and challenges that must be addressed to ensure it is used responsibly and equitably. From data privacy concerns to the risk of algorithmic bias, healthcare organizations and regulators must navigate complex ethical dilemmas as they integrate AI technologies into clinical practice. This section explores the key ethical issues and challenges surrounding the use of AI in healthcare and outlines potential solutions to mitigate risks.
Data Privacy and Security
One of the most significant ethical concerns surrounding the use of AI in healthcare is the protection of patient data. AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of patient data, including sensitive medical information, to make accurate predictions and decisions. As a result, healthcare organizations must prioritize data privacy and security to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse.
- Confidentiality: Patient confidentiality is a cornerstone of healthcare ethics. When AI is used to analyze medical records, imaging data, and genetic information, strict safeguards must be in place to protect patient identity. Data breaches or unauthorized access to personal health information could lead to devastating consequences for patients, including identity theft, discrimination, and loss of trust in healthcare providers.
- Data Ownership: Another important consideration is data ownership. Who owns patient data—the individual, the healthcare provider, or a third-party AI vendor? Establishing clear guidelines around data ownership and consent is critical to ensure that patients retain control over their personal information while enabling AI technologies to function effectively.
To mitigate privacy and security risks, healthcare organizations must implement robust cybersecurity protocols, ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., and obtain informed consent from patients before collecting or using their data for AI-driven purposes.
Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms
Another critical challenge is the potential for bias in AI algorithms. Machine learning models are trained on historical data, which may reflect existing biases in healthcare systems. If these biases are not addressed, AI can perpetuate and even amplify healthcare disparities, leading to unequal treatment for certain groups of patients.
- Bias in Training Data: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. If training data includes biases related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, or other demographic factors, the resulting algorithms may produce biased outcomes. For example, if an AI model is trained predominantly on data from one ethnic group, it may not perform as accurately for individuals from other ethnic backgrounds, leading to incorrect diagnoses or treatment recommendations.
- Discrimination and Health Inequality: The risk of AI exacerbating health inequalities is particularly concerning in populations that are already marginalized, such as low-income communities, racial minorities, and rural populations. AI systems must be carefully evaluated to ensure that they do not inadvertently discriminate against these groups, further entrenching existing health disparities.
To address these concerns, AI developers must ensure that their training datasets are diverse and representative of all patient populations. Additionally, transparency in algorithm development and regular audits of AI models can help identify and mitigate bias, promoting fairness in healthcare decision-making.
Accountability and Transparency
The question of accountability is another important ethical issue when it comes to AI in healthcare. As AI systems become more autonomous in making medical decisions, determining who is responsible when something goes wrong is a complex issue. In the event of a misdiagnosis, treatment error, or other adverse outcome, the role of the AI system, healthcare providers, and organizations must be clearly defined.
- Responsibility for AI Decisions: If an AI algorithm makes an incorrect decision that harms a patient, should the healthcare provider be held accountable, or should the blame lie with the creators of the AI system? This question raises concerns about liability and the role of AI in medical decision-making. Healthcare providers must maintain oversight and ensure that AI systems complement rather than replace human judgment.
- Transparency and Trust: Transparency is crucial for building trust in AI technologies. Healthcare professionals and patients must understand how AI systems arrive at their recommendations or decisions. If AI algorithms are viewed as “black boxes,” where their inner workings are not clear, patients may be reluctant to trust the technology, undermining its effectiveness and acceptance.
To ensure accountability and transparency, AI systems should be designed with explainability in mind. This means that healthcare providers should be able to understand how AI models make decisions and explain these decisions to patients in an accessible way. Furthermore, regulatory bodies must develop clear guidelines around the use of AI in healthcare, establishing accountability frameworks for developers, healthcare organizations, and providers.
Impact on the Healthcare Workforce
The integration of AI in healthcare also raises concerns about its impact on the workforce. While AI has the potential to improve efficiency and assist healthcare professionals, there are fears that automation could lead to job displacement and change the nature of work in healthcare.
- Job Displacement: As AI automates routine tasks such as administrative work, medical billing, and even certain diagnostic procedures, some healthcare roles may become obsolete. While AI can enhance productivity and reduce clinician burnout, there is concern about how this will affect jobs in the healthcare sector, particularly for administrative staff and even some clinicians in diagnostic fields like radiology.
- Changing Roles and Training: The implementation of AI may shift the roles and responsibilities of healthcare workers. For example, doctors and nurses may need to adapt to working alongside AI systems, using them as decision-support tools rather than relying solely on their own judgment. This requires significant investment in training and education to ensure that the workforce can effectively integrate AI into their practices without feeling overwhelmed or replaced.
To address these concerns, healthcare organizations must invest in workforce development and retraining programs to ensure that employees are equipped with the skills needed to work in an AI-enabled environment. Additionally, AI should be viewed as a tool to augment healthcare professionals’ capabilities rather than replace them, allowing them to focus on higher-value tasks such as patient care and complex decision-making.
Regulation and Governance of AI in Healthcare
The rapid development and deployment of AI in healthcare have outpaced regulatory frameworks, creating uncertainty about how to govern its use effectively. Without clear and consistent regulations, the risk of misuse or suboptimal outcomes increases.
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of standardized guidelines for developing and deploying AI in healthcare makes it difficult to ensure that AI systems are safe, effective, and ethical. Different countries have different regulations, and the lack of universal standards can lead to discrepancies in how AI technologies are implemented across healthcare systems.
- Regulatory Oversight: Governments and regulatory bodies must develop and enforce standards that ensure AI systems meet safety and efficacy criteria. Regulatory oversight is crucial to prevent the use of unsafe or ineffective AI tools, as well as to ensure that patient rights are protected throughout the AI lifecycle.
To address these issues, it is essential for healthcare stakeholders—governments, regulatory agencies, AI developers, and healthcare providers—to collaborate in establishing clear, evidence-based regulations and standards for AI in healthcare. This will help ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and safely, minimizing risks while maximizing their potential benefits.
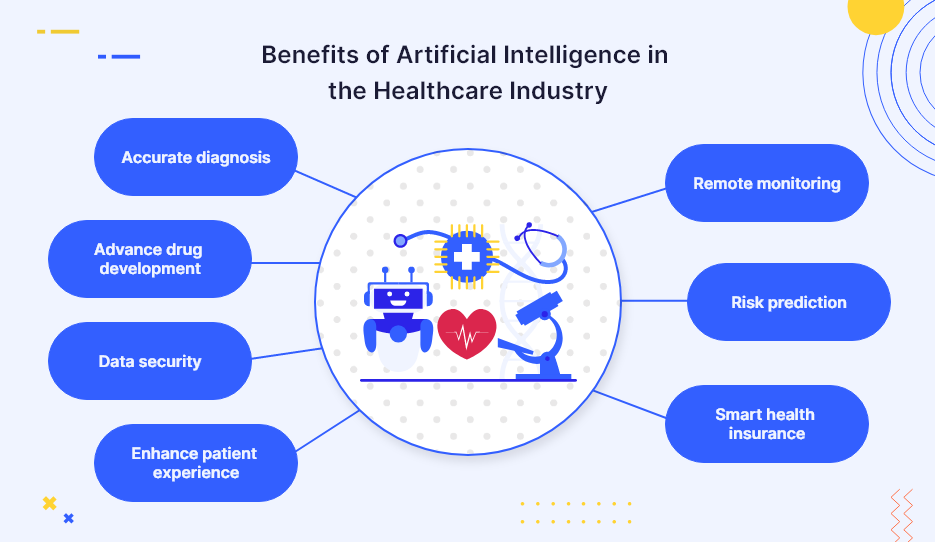
Section 5: The Future of AI in Healthcare
As AI continues to evolve, its potential to transform healthcare is vast and ever-expanding. The integration of artificial intelligence into healthcare systems is still in its early stages, but its trajectory suggests an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of medicine. From advancing diagnostic capabilities to revolutionizing patient care models, AI holds the key to addressing some of healthcare’s most pressing challenges. This section explores the future of AI in healthcare, focusing on emerging trends, opportunities for innovation, and the continued evolution of AI technologies.
Advancements in AI Technologies
The future of AI in healthcare will be characterized by increasingly sophisticated technologies that continue to push the boundaries of what is possible. Machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP) are just a few of the AI technologies that are expected to improve further in the coming years.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Deep learning, a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks, has already demonstrated remarkable capabilities in areas such as image recognition and natural language understanding. As these technologies advance, we can expect AI systems to become even more proficient at processing complex medical data, including medical imaging, genomics, and electronic health records (EHR). These advancements will allow AI to make more accurate and timely diagnoses and enhance predictive analytics for disease prevention and treatment.
- Explainable AI: One of the challenges of current AI applications in healthcare is the lack of transparency and explainability. As AI becomes more integrated into clinical decision-making, there will be a growing demand for explainable AI—systems that can offer clear, understandable explanations for their decisions. This will be crucial for gaining the trust of healthcare providers and patients, especially in high-stakes scenarios like diagnostic decision-making or treatment recommendations. Explainable AI will enable healthcare professionals to better understand and validate AI’s role in clinical practice.
- AI and Genomics: The role of AI in genomics is poised to expand rapidly. Advances in genome sequencing technology have made it possible to map human genomes more efficiently and affordably. AI’s ability to analyze large-scale genetic data can help identify genetic risk factors for diseases, predict how individuals will respond to treatments, and facilitate the development of personalized medicine. As the intersection of AI and genomics continues to advance, we can expect to see AI playing a significant role in precision medicine, particularly in cancer care and rare genetic disorders.
Personalized Medicine and AI-Driven Treatments
One of the most promising aspects of AI in healthcare is its potential to revolutionize personalized medicine. Personalized medicine involves tailoring medical treatments and interventions to the individual characteristics of each patient, such as their genetic profile, lifestyle, and medical history. AI is poised to take personalized medicine to the next level by enabling more precise and targeted treatment approaches.
- Genomic Medicine: AI’s ability to analyze complex genetic data will allow for more accurate predictions of disease risk and personalized treatment plans. By combining genomic data with other health data sources, AI can recommend the most effective treatments for individual patients, improving outcomes and reducing adverse reactions. For example, in cancer treatment, AI can help identify specific genetic mutations in tumors, allowing for more effective targeted therapies and immunotherapies that are tailored to the patient’s genetic makeup.
- AI in Drug Repurposing: AI is also being used to identify new uses for existing drugs, a process known as drug repurposing. By analyzing large datasets of clinical trial results, medical records, and scientific literature, AI can uncover hidden patterns that suggest how existing medications might be effective in treating diseases beyond their original purpose. In this way, AI can expedite the process of finding new treatments, especially for rare or complex diseases where new drug development has been slow.
- AI for Precision Surgery: Robotics and AI are set to transform surgical procedures through precision and real-time decision-making. AI-powered surgical robots, combined with augmented reality (AR) and machine learning, will be able to assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with higher accuracy and fewer complications. These advancements will lead to shorter recovery times, fewer surgical errors, and better patient outcomes.
AI and Population Health Management
AI has the potential to revolutionize how healthcare systems approach population health management. By analyzing data from diverse patient populations, AI can help identify health trends, predict disease outbreaks, and enable proactive interventions. These capabilities will allow healthcare systems to move beyond treating individual patients and focus on improving the health of entire communities.
- Predicting Public Health Trends: AI-powered tools will play a crucial role in predicting and managing public health issues such as disease outbreaks, epidemics, and pandemics. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical health data, environmental factors, and patient demographics to forecast potential outbreaks and help health organizations respond more swiftly. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, AI was used to predict the spread of the virus and guide containment efforts.
- Chronic Disease Management: Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma, account for a significant portion of healthcare costs and patient morbidity. AI can help manage chronic diseases by predicting flare-ups, monitoring patient adherence to treatment plans, and providing personalized recommendations for lifestyle changes. With AI’s help, healthcare providers can intervene earlier, potentially preventing hospitalizations and reducing the burden of chronic conditions on healthcare systems.
- Social Determinants of Health: AI can also address social determinants of health (SDOH) by analyzing non-medical factors such as socioeconomic status, education, housing, and access to healthcare. By incorporating these factors into predictive models, AI can help identify at-risk populations and ensure that interventions are targeted where they are most needed.
AI and the Future Healthcare Workforce
As AI continues to advance, the healthcare workforce will need to adapt to new technologies and ways of working. The role of healthcare professionals will evolve, with AI becoming an essential tool in improving both clinical decision-making and administrative functions. However, there will also be challenges in ensuring that the workforce is prepared to work alongside AI technologies.
- Augmenting Healthcare Professionals: AI will not replace healthcare workers, but it will augment their capabilities. For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can assist radiologists in detecting diseases in medical images, while AI algorithms can help physicians analyze patient data more effectively. Healthcare professionals will remain central to patient care, but their roles will be more focused on higher-level decision-making, patient interaction, and providing emotional support.
- AI Training and Education: As AI becomes more embedded in healthcare, training the workforce to use these tools effectively will be crucial. Healthcare professionals will need to develop a strong understanding of AI technology and how it can enhance their practice. This includes gaining the skills to interpret AI-generated insights, ensure that AI tools are used responsibly, and communicate AI-driven recommendations to patients. Institutions will need to offer ongoing education and upskilling programs to keep healthcare workers proficient in using AI technologies.
- Collaboration Between Humans and AI: The future of healthcare will be characterized by collaboration between AI and healthcare professionals, with each complementing the other’s strengths. AI will handle large-scale data analysis, routine tasks, and complex calculations, while healthcare providers will focus on areas requiring human empathy, ethical judgment, and communication. This partnership will enhance the overall patient experience and improve healthcare outcomes.
Global Access to Healthcare and Equity
AI has the potential to increase access to healthcare and improve health equity, particularly in underserved and resource-limited areas. AI-powered telemedicine, remote monitoring, and diagnostic tools can bridge gaps in healthcare access, providing high-quality care to populations that may otherwise lack resources or healthcare infrastructure.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: The global expansion of telemedicine, supported by AI, can provide healthcare access to individuals in rural and low-income areas, where there may be a shortage of healthcare providers. AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots can help triage patient concerns, reducing wait times and providing consultations to individuals who may not have access to in-person care.
- Affordable Healthcare Solutions: AI-driven diagnostic tools are helping lower the cost of healthcare by automating tasks that were once labor-intensive, such as interpreting medical imaging or processing lab results. This not only reduces costs for healthcare providers but also makes healthcare more affordable for patients, particularly in lower-income regions.
- Equitable AI Development: To ensure that AI benefits all populations, it is crucial to develop AI systems that are inclusive and equitable. This includes using diverse datasets in AI training to ensure that algorithms work effectively across all demographic groups, as well as ensuring that AI solutions are accessible to populations in low-resource settings.
Conclusion
Summary of AI’s Transformative Impact on Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in healthcare, reshaping the landscape of how medical professionals diagnose, treat, and care for patients. Through the power of machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced data analytics, AI is revolutionizing the healthcare industry in profound ways. In diagnostics, AI-driven tools are enabling earlier detection of conditions, improving the accuracy of medical imaging analysis, and enhancing clinical decision-making. In treatment, AI is facilitating personalized medicine, allowing for targeted therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles, improving patient outcomes, and reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Furthermore, AI is enhancing patient care by streamlining workflows, automating routine tasks, and providing decision support that enables healthcare professionals to focus on more complex, value-driven activities. From predictive algorithms that help manage chronic conditions to virtual assistants that offer real-time patient support, AI is improving both patient experience and operational efficiency. With the ability to analyze vast amounts of health data, AI is also helping healthcare systems optimize resources, reduce costs, and ensure timely interventions. In all these ways, AI is proving to be an essential partner in the future of healthcare, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in medical practice.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its promise, the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare comes with several challenges that need to be addressed. As AI becomes an integral part of healthcare systems, issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and regulatory uncertainty remain significant concerns. Ensuring that patient data is protected, securing AI systems against cyber threats, and creating robust frameworks for transparency in decision-making are critical to mitigating potential risks. Moreover, the potential for biases in AI algorithms could exacerbate existing healthcare disparities, and special care must be taken to ensure that AI solutions are inclusive and equitable for all patient populations.
Equally important are the challenges surrounding workforce adaptation and the ethical implications of AI in clinical practice. Healthcare professionals will need continuous education and training to work effectively with AI tools, and there must be clear guidelines on accountability when AI decisions lead to negative outcomes. Research, regulation, and ethical practices must evolve in parallel with AI development to ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and with the best interests of patients in mind.
Call to Action
As AI continues to evolve and make inroads in healthcare, it is crucial that healthcare professionals, organizations, and policymakers embrace this transformative technology while remaining vigilant about its potential risks. Healthcare providers must engage with AI tools not just as passive recipients but as active collaborators, ensuring that AI is integrated thoughtfully into their practices. Organizations should invest in training programs that equip healthcare workers with the skills needed to work alongside AI systems, fostering a culture of innovation that prioritizes both human expertise and technological advancements.
Policymakers and regulators must continue to work toward developing robust frameworks that guide the ethical use of AI in healthcare. This includes creating guidelines for data protection, ensuring fairness in AI algorithms, and fostering public trust through transparency. Collaboration among AI developers, healthcare practitioners, and regulatory bodies will be essential to maximizing the benefits of AI while minimizing risks.
Finally, the opportunity to improve healthcare outcomes for all patients is within reach, but it requires commitment, careful planning, and a willingness to embrace the future. The integration of AI into healthcare is not just about improving individual patient outcomes but also about building a more efficient, equitable, and sustainable healthcare system for the future. By continuing to explore, refine, and adopt AI technologies, we can move closer to a healthcare environment that is more personalized, proactive, and ultimately, more effective for patients worldwide.